
If your child complains of tooth pain or a toothache, you will want to do whatever you can to help them feel better. You will need to determine what is causing their pain so that you can find the best solution to relieve it.
To help you figure it out, ask your child questions about what they are experiencing. See if they can point out the area of their mouth that is painful. Look in your child's mouth to check for any damaged teeth, swelling or bleeding.
Be sure to schedule a dental appointment for your child. When you make the appointment, provide as much detail as you can, and ask if your dentist has any advice for pain relief to help your child right away.
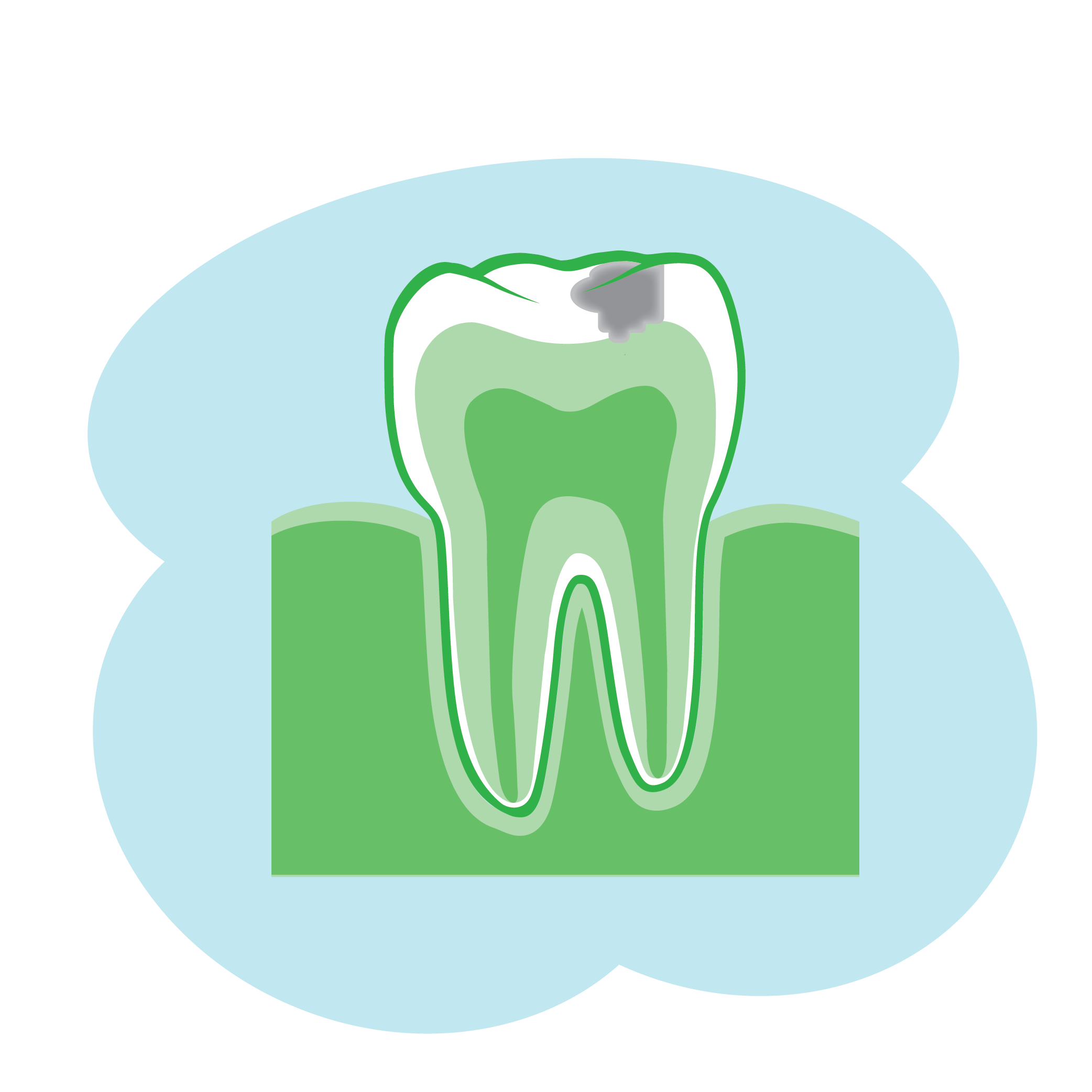
Common dental problems that can result in a toothache include:
- Teething
- Tooth decay
- Chipped teeth or cracked enamel
- Food stuck between teeth or under the gums

Here are a few ways you can help to temporarily relieve your child’s pain:
For teething:
- Rub their gums with your clean fingers or a wet cloth.
- Give them a cool/chilled teething ring.
- Give a small amount of over the counter pain medication like ibuprofen or Tylenol, as directed by your doctor.
For other types of pain:
- Help your child to floss. Flossing will clear anything stuck between your child’s teeth or around their gums, but be extra careful so that you don’t accidentally worsen the pain or cause more irritation.
- Rinse their mouth with warm salt water. Put a small amount (about a teaspoon) of salt into a glass of warm water and have your child rinse for about 30 seconds. Make sure water is not hot or cold since extreme temperatures could make the pain worse.
- Use a cold compress. Gently hold a cold compress against the outside of your child’s teeth or mouth near the painful spot for a few minutes at a time.
- Give them a small amount of over the counter pain medication like ibuprofen or acetaminophen, as directed by your doctor.
Make sure you follow any recommendations given by your dentist, and help your child maintain their normal oral health routine including brushing and flossing.
Posted: February 8, 2020
Revised: February 1, 2022
This information in this post is for general educational purposes only and does not warrant or represent any information as related to health as specifically appropriate for you. It is not intended to be medical advice or replace the relationship that you have with your health care providers. You should always seek medical advice on any diagnosis or treatment from a qualified health care provider. The information is provided “as is” without any representations or warranties, express or implied.








